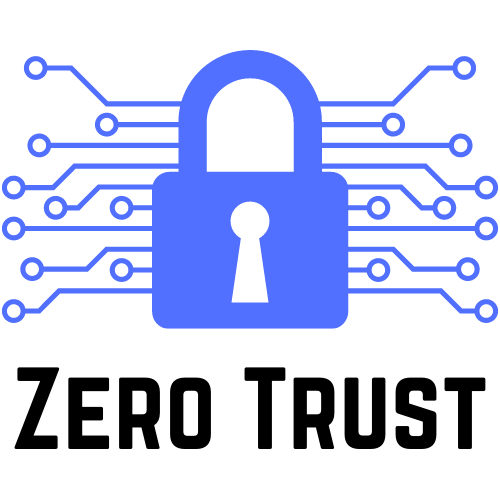
There has been a lot of talk about Zero Trust, so let me try to give an overview. I’ll finish up with an example from iboss and a deep dive from AWS. First, think of it more as a methodology and not a new product category. It is a cybersecurity approach that has gained attention for its ability to prevent data breaches. It is not just for enterprise or commercial use. Educational institutions, both in K-12 and higher education, and the public sector find value in implementation as well. It’s built on the principle of “never trust, always verify” (NOT: trust, but verify). Zero Trust aims to protect digital environments by leveraging the cloud. It rethinks how we implement identity and access management and network security. Capabilities include inspection, network segmentation, preventing lateral movement, providing threat prevention, and simplifying granular user-access control.
Beginnings
It was also born out of the need to think beyond just protecting the perimeter with a firewall because trusting everyone inside the firewall was not working. Also, more resources are outside the firewall (i.e. in the cloud) and more users aren’t behind the firewall (i.e. at home or Starbucks). The approach uses information derived from Identity, Credential, and Access Management (ICAM) systems. ICAM consistently verifies all users, devices, applications, and data based on context and user activity. Have you had a website that you use a lot reverify you because you’re not in your usual place? That’s Zero Trust at work.
“Zero trust is a way of thinking, not a specific technology or architecture,” says Gartner Distinguished VP Analyst Neil MacDonald. “It’s really about zero implicit trust, as that’s what we want to get rid of.”
Gartner
ZTNA
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) extends this strategy. ZTNA provides remote access to applications and services based on defined access control policies. Policies combine role-based, granular, encrypted access controls with post-connect threat monitoring. It involves micro-segmentation of the network (micro perimeters).
Existing infrastructure and technology work for Zero Trust. There are no specific products! Rather it’s an integral part of a complete modern cybersecurity architecture. The approach enables complete end-to-end visibility and rich policy-based controls to mitigate even the most sophisticated threats.
Don’t Do It Yourself
Leading solution providers now incorporate the tenets of ZTNA. Comprehensive, end-to-end platform architectures to address even more use cases come from a single vendor or a mix of “best of breed” suppliers. This approach offers educational institutions and the public sector several advantages. Context-based access encompasses all users, all devices, all applications, and all workloads. Zero Trust provides uncompromising security by continuously examining all content to prevent both known and unknown malicious activity in real-time.
Furthermore, it enables global and consistent access security everywhere, regardless of the location of a user, device, or application. This is best achieved through physical, virtual, and cloud-native firewalls that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to enable context-based access on-premises, in the cloud, in remote work environments, or across campuses. Simply put, all traffic, whether to or from campus, the office, home, or, say, a cafe, goes through a cloud firewall and a series of checks.
Example: iboss Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
The iboss Zero Trust SASE allows all protected resources within an organization to be labeled and categorized, including Security Objectives and Impact Levels. This provides organizations with a clear understanding of where sensitive applications and data reside while providing insight into what users and assets are interacting with those protected resources. The iboss Service follows the NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) and implements tenets from the NIST 800-207 Zero Trust Architecture Special Publication.
Components

Overall, Zero Trust represents a convergence of secure network transport with a cloud-native security stack that includes components such as ZTNA, Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), Secure Web Gateway, Firewall-as-a-Service), Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN), and micro-segmentation. But don’t think of it as a “rip and replace“, but an additive approach to what you’re already doing.
Deep Dive: What is Zero Trust on AWS
AWS describes Zero Trust as a security model that emphasizes strong identity verification and authorization rules before granting access to data, applications, and systems.

Zero Trust is not solely based on network location and operates within highly flexible identity-aware networks, which reduce surface area and eliminate unneeded pathways to data. AWS provides several identity and networking services that can be used as building blocks for implementing Zero Trust. To move towards Zero Trust, AWS says, evaluate the workload portfolio and apply Zero Trust concepts, such as rethinking identity, authentication, and context indicators.
AWS, itself, implements Zero Trust in interesting ways. When using the console every API (application programming interface) call is authenticated. Also, when using services in an account, the services do not automatically have access to other services. You must set up a role that is authenticated when that service is instantiated and every call it maqkes. Security Groups and Network Access Control Lists are another way AWS implements Zero Trust. They can limit traffic north-south and east-west. Remember, Zero Trust is a process and architecture, not a product.
To dive deeply read Zero Trust architectures: An AWS perspective and watch the re:Invent session Zero Trust: Enough talk, let’s build better security.

By adopting a Zero Trust approach, educational institutions and the public sector can strengthen their cybersecurity posture and better protect themselves against the ever-evolving threat landscape. Tech Reformers is a consultancy focused on education and the public sector that can help assess your needs.