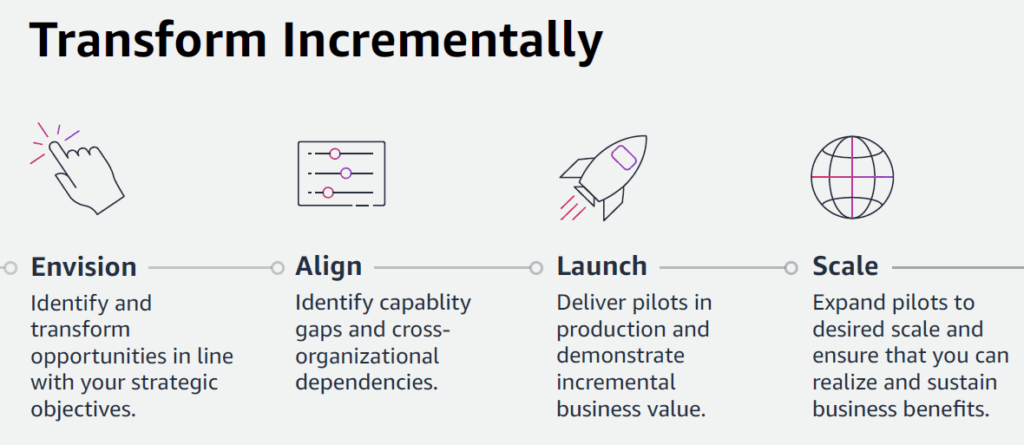
In today’s digital landscape, data protection is paramount. One of the most effective strategies for safeguarding your critical information is implementing air-gapped backups. This blog post will explore the benefits of air-gapped backups and how AWS is making this process more efficient and secure.
The Power of Air-Gapped Backups
Air-gapped backups provide an extra layer of security by creating a physical or logical separation between primary systems and backup data. Here’s why they’re crucial:
- Enhanced Security: By isolating backup data, you significantly reduce the risk of cyber attacks, ransomware, and unauthorized access.
- Data Integrity: Air-gapped backups ensure that your data remains intact and unaltered, providing a reliable restore point in case of emergencies.
- Compliance: Many industries require air-gapped backups to meet regulatory standards and protect sensitive information.
- Disaster Recovery: In the event of a catastrophic failure or breach, air-gapped backups offer a clean, uncompromised copy of your data.

AWS Backup Audit Manager: Streamlining Air-Gapped Backup Auditing
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has taken air-gapped backup security to the next level with its latest feature in AWS Backup Audit Manager. This new control allows you to audit and verify if your resource’s backup data is stored in a logically air-gapped vault.
Key Features:
- Automated Daily Audits: Once enabled, the control runs automatically each day, ensuring continuous monitoring of your air-gapped backups.
- Customizable Time Frames: Set specific time frames for backup copying, tailored to your business needs and compliance requirements.
- Comprehensive Resource Coverage: Apply the control to your selected AWS resources, ensuring thorough protection across your infrastructure.
- Auditor-Ready Reports: Generate detailed reports to demonstrate compliance with organizational and industry-specific regulations.
Getting Started with AWS Backup Audit Manager
Implementing this powerful feature is straightforward:
- Access the AWS Management Console
- Enable the new control in existing AWS Backup Audit Manager frameworks or create a new one.
- Specify your desired time frame and select the resources to monitor.
- Let AWS Backup Audit Manager handle the rest, providing you with daily audits and actionable insights.
Availability and Pricing
AWS Backup Audit Manager air gap feature is just out and is now available in 2 US regions:
- US East (Ohio, N. Virginia)
- US West (N. California, Oregon)
Next Steps
Air-gapped backups are a critical component of a robust data protection strategy. With AWS Backup Audit Manager’s new control for auditing logically air-gapped vaults, organizations can enhance their security posture, ensure compliance, and gain peace of mind knowing their backups are truly isolated and protected.
Take the next step in securing your data by leveraging AWS Backup Audit Manager today. Visit the AWS Backup product page and contact Tech Reformers to learn more and get started on your journey to bulletproof backup security.